5 min read
How to Enable Kdump in Warewulf Nodes

Introduction
Kdump utilizes kexec to swiftly boot into a dump-capture kernel whenever a memory dump of the system kernel is required, such as during a system panic. This process preserves the system kernel's memory image across a reboot, making it accessible to the dump-capture kernel.
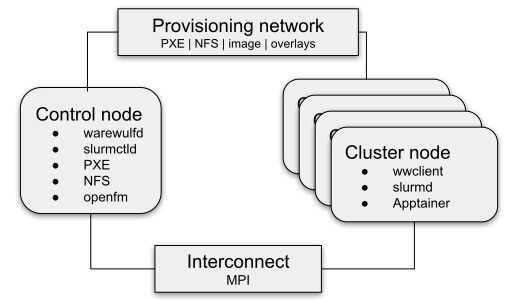
Getting kdump working on stateless nodes isn’t impossible; you just need to know how Warewulf handles boot images and kernel args. In this guide, you will learn how to enable kdump on one of your Compute Nodes in your Warewulf cluster. This is essential for when a kernel panic occurs and for performing an in-depth analysis at the kernel level.
Prerequisites
This guide assumes that a Warewulf server is successfully installed and nodes are able to boot from a Rocky Linux image.
In many cases, the kdump service is installed and activated by default on new Linux installations, but some installation options do not have to install or enable kdump by default.
If you do not know whether kdump is installed on your system, you can "shell into" an image with wwctl image shell, like the example below. For Warewulf 4.5.x versions, you can use wwctl container shell.
[root@Warewulf ~]# wwctl image shell rockylinux-9
Image build will be skipped if the shell ends with a non-zero exit code.
From there, you can check if the RPM has been installed by running rpm -q kexec-tools:
[warewulf:rockylinux-9] /# rpm -q kexec-tools
package kexec-tools is not installed
If you need to install kexec-tools, please run the command dnf install kexec-tools. This command secures the installation of the userspace tools for kexec:
[warewulf:rockylinux-9] /# dnf install kexec-tools
Last metadata expiration check: 0:01:12 ago on Wed Mar 5 18:07:55 2025.
Dependencies resolved.
=============================================================================================================================================================================================
Package Architecture Version Repository Size
=============================================================================================================================================================================================
Installing:
kexec-tools x86_64 2.0.27-16.el9_5.1 baseos 477 k
...
Complete!
Installation instructions
Configure kdump
The Linux kernel accepts several boot-time arguments. For example, Warewulf currently specifies the following arguments by default: quiet crashkernel=no vga=791 net.naming-scheme=v238.
You can specify a different set of kernel arguments for a node or profile using --kernelargs. This value is recorded on a node or profile as the Kernel.Args field.
To set this at the profile level, run this command:
wwctl profile set default --kernelargs 'quiet,crashkernel=512M,vga=791,net.naming-scheme=v238'
Similarly, to set this at the node level, run this command:
wwctl node set node01 --kernelargs 'quiet,crashkernel=512M,vga=791,net.naming-scheme=v238'
To specify the memory reserved for the kdump kernel, set the crashkernel= option to the required memory value. For example, to reserve 128 MB of memory, you can use crashkernel=128M.
NOTE: For newer Warewulf versions, kernel args field is set as a list to be able to combine them between profiles and nodes; therefore, these values may get appended. You potentially have to negate default values by adding "~". An example is: ~crashkernel=no.
Changing the excludes file inside the container to allow copying the /boot directory to the nodes
Warewulf can exclude files from an image to prevent them from being delivered to the compute node. This is typically used to reduce the size of the image when some files are unnecessary. Patterns for excluded files are read from the file /etc/warewulf/excludes in the image itself. For example, the default Rocky Linux images exclude these paths:
/boot/
/usr/share/GeoIP
To remove /boot/ from the excludes file, shell into the image:
[root@Warewulf ~]# wwctl image shell rockylinux-9
Image build will be skipped if the shell ends with a non-zero exit code.
[warewulf:rockylinux-9] /# sed -i '/\/boot\//d' /etc/warewulf/excludes
[warewulf:rockylinux-9] /# cat /etc/warewulf/excludes
/usr/share/GeoIP
Since kdump needs the vmlinuz file to boot the dump kernel, you need to add a symlink to /usr/lib/modules/<kernel_version>/<vmlinuz file>, as this file is not present on /boot:
[warewulf:rockylinux-9] /# KERNEL_VERSION=$(ls /usr/lib/modules | head -n 1)
ln -s /usr/lib/modules/$KERNEL_VERSION/vmlinuz-$KERNEL_VERSION /boot/vmlinuz-$KERNEL_VERSION
[warewulf:rockylinux-9] /# ls /boot/ | grep vmlinuz
vmlinuz-5.14.0-503.19.1.el9_5.x86_64
Configuring the kdump target
When a kernel crash is captured, the core dump can be stored in various ways: as a file in a local file system, directly on a device, or sent over a network using the NFS (Network File System) or SSH (Secure Shell) protocols. Only one of the three options can be configured at a time. By default, the vmcore file is stored in the /var/crash directory of the local file system. To verify this, check the /etc/kdump.conf file's contents. In this example, NFS is used, since the Warewulf nodes will clear anything in memory after a reboot, and anything added to /var/crash will be removed.
An example from the /etc/kdump.conf file:
# nfs <nfs mount>
# - Will mount nfs to <mnt>, and copy /proc/vmcore to
# <mnt>/<path>/%HOST-%DATE/, supports DNS.
Configure kdump manually on the container
Shell into the image and run the following commands:
[warewulf:rockylinux-9] /# grep -v ^# /etc/kdump.conf
auto_reset_crashkernel yes
path /var/crash
core_collector makedumpfile -l --message-level 7 -d 31
[warewulf:rockylinux-9] /# vi /etc/kdump.conf
# Edit the fields accordingly
# If adding nfs please comment path
auto_reset_crashkernel yes
#path /var/crash
nfs nfs_server_ip:/kdump/path
core_collector makedumpfile -l --message-level 7 -d 31
Configuring kdump using overlays
To create the kdump overlay, please run:
$ wwctl overlay create kdump
Edit the kdump.conf.ww file (this command will create the overlay template):
$ wwctl overlay edit --parents kdump /etc/kdump.conf.ww
Add the following configuration after the # This file is autogenerated by warewulf line:
auto_reset_crashkernel yes
core_collector makedumpfile -l --message-level 7 -d 31
{{ if .Tags.kdump_nfs_location }}
nfs {{ .Tags.kdump_nfs_location }}
{{ else }}
path /var/crash
{{ end }}
Check that the new changes were applied successfully:
wwctl overlay show kdump /etc/kdump.conf.ww
Display the changes on a node to confirm it is working as expected:
$ wwctl overlay show -r node01 kdump /etc/kdump.conf
backupFile: true
writeFile: true
Filename: /etc/kdump.conf
# This is a Warewulf Template file.
#
# This file (suffix '.ww') will be automatically rewritten without the suffix
# when the overlay is rendered for the individual nodes. Here are some examples
# of macros and logic which can be used within this file:
#
# Node FQDN = node01
# Node Cluster = oso
# Network Config = <no value>, <no value>, etc.
#
# Go to the documentation pages for more information:
# https://warewulf.org/docs/main/contents/overlays.html
#
# Keep the following for better reference:
# ---
# This file is autogenerated by warewulf
auto_reset_crashkernel yes
core_collector makedumpfile -l --message-level 7 -d 31
path /var/crash
Change the tag to add the NFS path by using the --tagadd flag. In the following example, the path used was 172.16.131.5:/var/crash/:
$ wwctl profile set default --tagadd kdump_nfs_location=172.16.131.5:/var/crash/
Are you sure you want to modify 1 profile(s): y
Render the changes on a node to confirm the changes:
$ wwctl overlay show -r node01 kdump /etc/kdump.conf
# Removing the extra lines to shorten the output
...
nfs 172.16.131.5:/var/crash/
Add the newly created overlay to the default profile, and boot the node:
wwctl profile set default -O $(wwctl profile list default -a | grep SystemOverlay | awk '{print $3,kdump}')
Testing the kdump configuration
⚠️ WARNING The commands below cause the kernel to crash. Use caution when following these steps, and by no means run them on a production system.
To test the configuration, ssh into the node, and make sure that the service is running:
$ systemctl status kdump.service
#If the service is active, please run the following commands:
$ echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/sysrq
$ echo c > /proc/sysrq-trigger
The above commands force the Linux kernel to crash, and the address-YYYY-MM-DD-HH:MM:SS/vmcore file is copied to the location you have selected in the configuration (that is, to /var/crash/ by default).
References & related articles
Built for Scale. Chosen by the World’s Best.
1.4M+
Rocky Linux instances
Being used world wide
90%
Of fortune 100 companies
Use CIQ supported technologies
250k
Avg. monthly downloads
Rocky Linux